Top 5 myths & facts about posterior placenta

During pregnancy, the placenta is extremely important. The placenta is an important organ in pregnancy that supplies oxygen and nutrients to the baby via the umbilical cord.
What is the function of the placenta?
During pregnancy, the placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus. A growing baby gets oxygen and nutrients from this structure. It also cleans the baby's blood of waste materials. The placenta adheres to the uterine wall, and the umbilical cord of the newborn emerges from it. The organ is normally attached to the uterus's top, side, front, or back. The placenta may connect in the lower part of the uterus in rare situations. A low-lying placenta is what it's called when this happens (placenta previa).
What is the location of the placenta?
The placenta can be placed in any of the following ways:
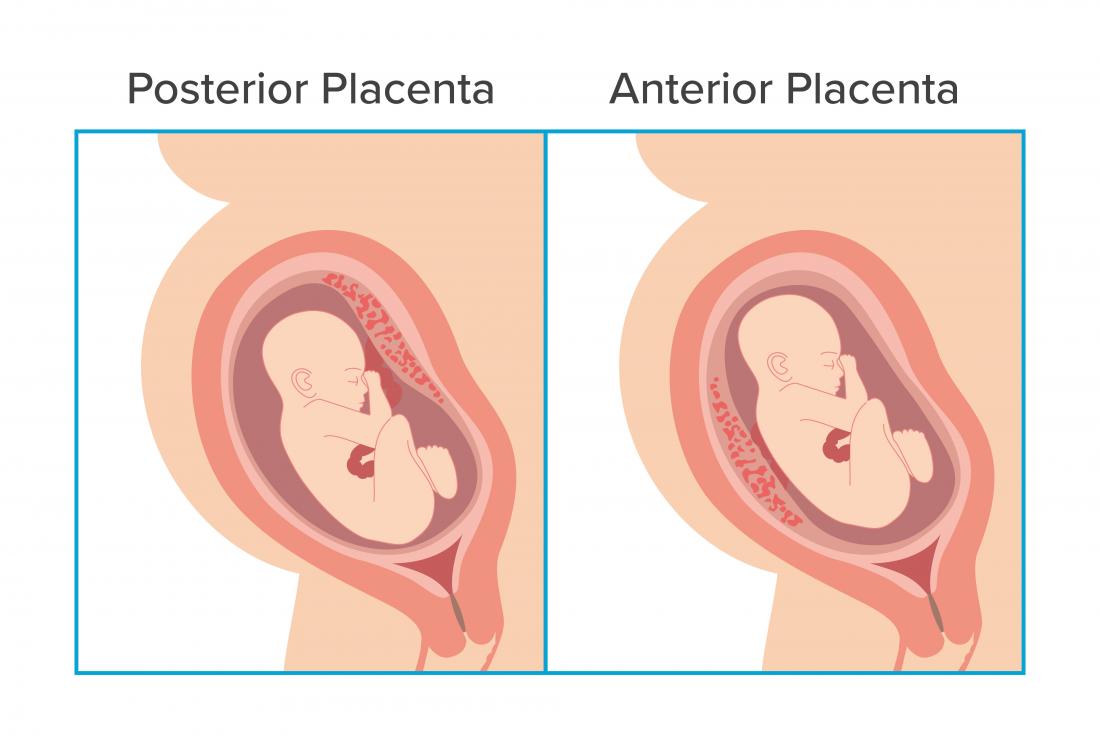
Anterior Placenta: This indicates that the placenta is close to the uterus's front wall.
Posterior Placenta: The placenta is linked to the uterus's back wall. Because 'fundal' refers to the top of the fundus/uterus, the phrase 'fundal posterior' refers to the placenta being nearer the top and back of the uterine wall.
ALSO READ - Amazing Benefits Of Apple Juice For Your Hair, Skin, And Health
5 Myths to know about Posterior Placenta
- The gender of the foetus is linked to the posterior placenta: There is no scientific proof that a posterior placenta indicates whether the baby is a boy or a girl. A fundal posterior placenta and an anterior placenta are the same. "A few studies may have suggested a link between placental location and gender, but no references to this notion have been found in the medical literature."
- Fetal movement is heightened by the posterior placenta: "A few anecdotal stories imply that moms experience greater kicks early in pregnancy when the placenta is positioned in the back or subtle kicks due to an anterior placenta cushioning the kicks, but no scientific study supports these assertions."
- Preterm labour is more likely with a posterior placenta: The findings that a posterior placenta increases the risk of preterm delivery and an anterior placenta increases the risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension, gestational diabetes, or intrauterine growth restriction are not supported by any national or international obstetrics guidelines.
- The optimal position for the placenta is posterior: This is thought to be the best posture because it allows the baby to migrate into the proper position.
- The posterior placenta has an effect on the likelihood of a normal delivery: "A vaginal birth is possible as long as the placenta does not block the cervix, which stops the baby from going through the birth canal and results in painless bleeding."
"In this case, a cesarean section is the safest way to deliver the baby."
The position of the placenta might differ from one woman to the next and from one pregnancy to the next.

